Auto Screen Repair issues can be frustrating, especially when they lead to a continuous loop of failed attempts. At AUTO-REPAIR-TRAINING.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive insights into understanding and resolving such issues, ensuring you can get your system back on track. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and effective solutions to fix the auto screen repair loop, and also explore opportunities for advanced learning in auto repair, including potential career paths with ASE certification, business plan development, and step-by-step guidance to empower your journey.
Contents
- 1. What Causes a Windows Auto Screen Repair Loop?
- 2. How to Fix a Windows Auto Screen Repair Loop
- 2.1 Blue Screen – Use System Restore to Undo Changes
- 2.2 Blue Screen – Run Built-In System Repair Tools
- 2.3 Black Screen – Run Antivirus Scans and Update Drivers
- 2.4 Black Screen – Disable Auto Screen Repair Loop
- 2.5 Repair Boot Configuration Data
- 2.6 Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware
- 2.7 Perform a Clean Boot
- 3. Other Windows Errors and Repair Solutions
- 4. Exploring Career Paths in Auto Repair
- 4.1 Entry-Level Positions
- 4.2 Mid-Level Positions
- 4.3 Advanced Positions
- 4.4 Specialized Roles
- 4.5 Business Ownership
- 5. Essential Skills for Success in Auto Repair
- 5.1 Technical Skills
- 5.2 Soft Skills
- 5.3 Business Skills
- 6. Training and Certification Programs
- 6.1 Vocational Schools
- 6.2 Community Colleges
- 6.3 Apprenticeship Programs
- 6.4 ASE Certification
- 6.5 Online Training Programs
- 7. Steps to Open Your Own Auto Repair Shop
- 7.1 Develop a Business Plan
- 7.2 Secure Funding
- 7.3 Choose a Location
- 7.4 Obtain Licenses and Permits
- 7.5 Purchase Equipment and Supplies
- 7.6 Hire and Train Staff
- 7.7 Market Your Business
- 8. Understanding Auto Repair Business Finances
- 8.1 Startup Costs
- 8.2 Operating Expenses
- 8.3 Revenue Streams
- 8.4 Pricing Strategies
- 8.5 Financial Metrics
- 9. Current Trends in the Auto Repair Industry
- 9.1 Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 9.2 Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- 9.3 Digitalization
- 9.4 Customer Experience
- 10. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- 10.1 Competition
- 10.2 Staffing
- 10.3 Rising Costs
- 10.4 Customer Satisfaction
- 10.5 Regulatory Compliance
- FAQ: Auto Screen Repair & Auto Repair Career
1. What Causes a Windows Auto Screen Repair Loop?
The Windows auto screen repair loop usually happens because of damaged or missing system files, issues with the Boot Manager, hardware that doesn’t work well together, or problems during updates. Sometimes, even a flawed Windows update can cause your computer to get stuck in a restart loop.
Identifying the signs early is crucial. You might see a black screen with messages like “Diagnosing your PC” or “Preparing automatic repair” that never seem to finish. Alternatively, you might get a blue screen that says, “Automatic repair couldn’t repair your PC” or “Your PC did not start correctly.”
Understanding these signs helps you figure out what’s wrong. Sometimes, the problem can even be a broken Windows update, causing the system to fail repeatedly. Regular maintenance and awareness can prevent these issues, ensuring your system remains stable.
2. How to Fix a Windows Auto Screen Repair Loop
Fixing the auto screen repair loop in Windows means using different solutions based on whether you see an unresponsive black screen or a blue screen with an error message. The methods below offer strategies to help you deal with and fix this problem.
2.1 Blue Screen – Use System Restore to Undo Changes
System Restore can fix the problem by returning your operating system to a previously working state, which replaces corrupted files that might be causing the loop.
- On the auto screen repair blue screen, click on “Advanced options”.
- Go to “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced Options” > “System Restore”.
- Pick a restore point that was made before the problem started. Windows 10 usually creates these points during updates, driver installations, or when you install apps.
- Click “Next” and wait for the restore to finish.
- Restart your computer.
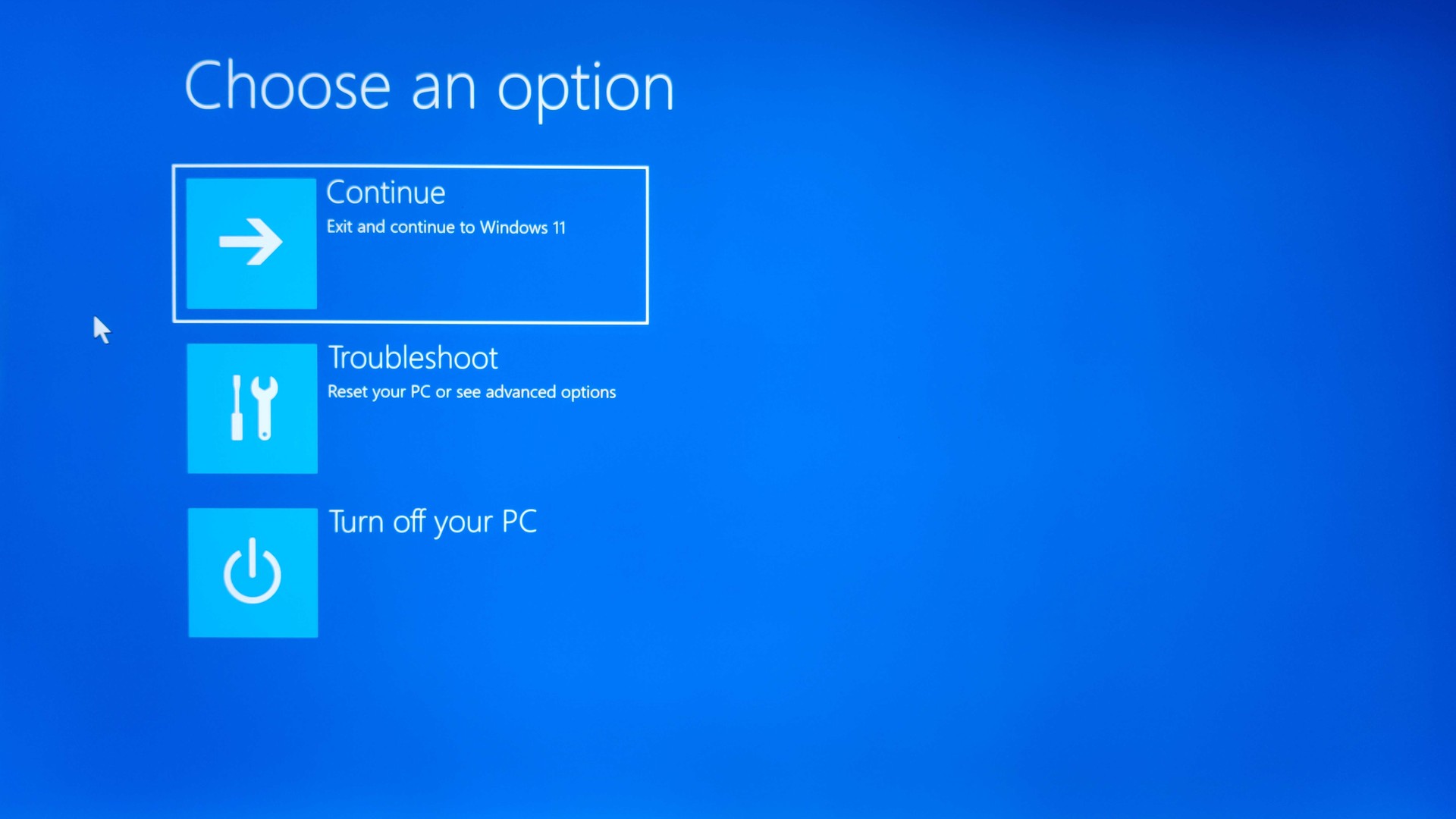 Screenshot of the recovery menu in Windows 10 and Windows 11
Screenshot of the recovery menu in Windows 10 and Windows 11
2.2 Blue Screen – Run Built-In System Repair Tools
Windows has two powerful tools to check for and fix missing or corrupted system files: System File Checker (SFC) and CHKDSK. These tools can help resolve underlying issues causing the auto screen repair loop.
- Restart your computer and press the “F8” key to open the Windows troubleshooting menu.
- Select “See advanced repair options”.
- Click “Troubleshoot” and then “Advanced options”.
- Open “Command Prompt”.
- In the Command Prompt, type “chkdsk /r c:” and press Enter. This will scan for and fix disk errors.
- Next, type “sfc /scannow” and press Enter. This will check and repair the integrity of your system files.
- Type “exit” to close the Command Prompt, then restart your computer.
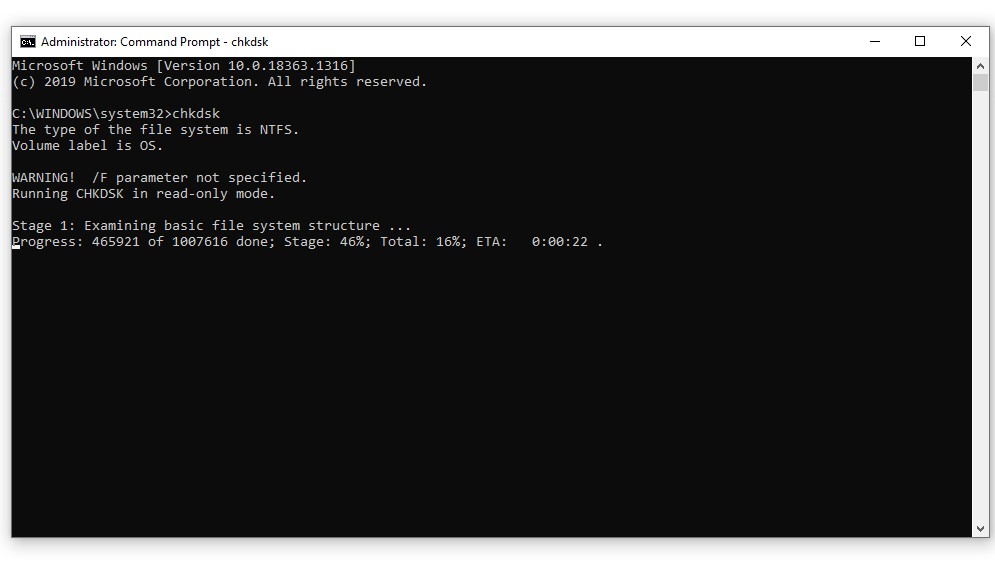 Screenshot of the chkdsk command running in Command Prompt on Windows 10
Screenshot of the chkdsk command running in Command Prompt on Windows 10
2.3 Black Screen – Run Antivirus Scans and Update Drivers
Using Safe Mode allows you to uninstall problematic device drivers, revert recent Windows updates, or remove any malware causing the issue. Follow these steps:
- Turn off your computer.
- Boot using Windows Installation Media and choose “Repair your computer” from the setup window. You can download and install Windows Installation Media from Microsoft.
- Go to “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Startup Settings”, and select a Safe Mode option.
- Once in Safe Mode, run antivirus software to check for malware, uninstall any incompatible software, and update your device drivers.
2.4 Black Screen – Disable Auto Screen Repair Loop
If nothing else works, you can turn off the auto screen repair feature:
- Insert a Windows installation disc or USB drive.
- Boot from the installation media, choose your language, and click “Next”.
- Click on “Repair your computer” > “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced Options” > “Command Prompt”.
- In Command Prompt, type “bcdedit /set {current} recoveryenabled No” and press Enter.
- Type “exit” and press Enter.
2.5 Repair Boot Configuration Data
Sometimes, the auto screen repair loop happens because the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) is corrupted. To fix this:
-
Insert a Windows installation disc or USB drive.
-
Boot from the installation media and select “Repair your computer”.
-
Click “Troubleshoot” > “Advanced options” > “Command Prompt”.
-
In Command Prompt, type the following commands. Press Enter after each command and wait for it to finish:
- bootrec /fixmbr – Repairs the Master Boot Record.
- bootrec /fixboot – Writes a new boot sector.
- bootrec /scanos – Scans for Windows installations.
- bootrec /rebuildbcd – Rebuilds the Boot Configuration Data.
These commands can fix issues with corrupted boot files that cause the auto screen repair loop.
2.6 Update BIOS/UEFI Firmware
Outdated or corrupted BIOS/UEFI firmware can cause boot problems. Updating the firmware can sometimes fix the auto screen repair loop:
- Identify Your BIOS/UEFI Version: Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings (usually by pressing Del, F2, or F10 during startup).
- Check Manufacturer’s Website: Go to your motherboard manufacturer’s website to find the latest firmware version.
- Compare Versions: If there’s a newer version, download it and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for updating.
2.7 Perform a Clean Boot
A clean boot starts Windows with only the essential drivers and startup programs, which can help you find out if background programs are causing the problem. To do a clean boot:
- Access System Configuration: Press Win + R, type msconfig, and press Enter.
- Selective Startup: In the “General” tab, choose “Selective startup” and uncheck “Load startup items.”
- Disable Services: Go to the “Services” tab, check “Hide all Microsoft services,” then click “Disable all.”
- Disable Startup Items: Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), go to the “Startup” tab, and disable all items.
- Restart Your Computer: Apply the changes and reboot.
If the problem is fixed, gradually turn the services and startup items back on to find the one that’s causing the issue.
3. Other Windows Errors and Repair Solutions
Besides the auto screen repair loop, Windows users often face other problems like the Blue Screen of Death (BSoD). This critical error can happen because of low disk space, faulty device drivers, or damaged hard disks. Fixing the BSoD usually means checking for Windows updates, uninstalling problematic drivers, and making sure you have enough storage space.
Other common Windows errors include problems updating between operating systems, storage limits after upgrading, and too many notifications in Windows 10. To handle these issues, regularly clear unnecessary files to free up disk space, manage startup programs to improve system performance, and adjust notification settings to reduce interruptions. Also, using the built-in troubleshooters can help find and fix underlying problems, making your experience smoother.
4. Exploring Career Paths in Auto Repair
The auto repair industry offers various career paths, from entry-level technician roles to specialized positions and business ownership. Here’s an overview of the opportunities available:
4.1 Entry-Level Positions
- Automotive Technician Apprentice: Assists experienced technicians, learns basic maintenance and repair tasks, and gains hands-on experience.
- Lube Technician: Performs oil changes, tire rotations, and other minor services, providing a starting point for learning about vehicle maintenance.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for automotive service technicians and mechanics was $46,830 in May 2021. Entry-level positions typically start lower but offer opportunities for advancement with experience and training.
4.2 Mid-Level Positions
- Automotive Technician: Diagnoses and repairs vehicle systems, including engines, transmissions, brakes, and electrical systems.
- Service Advisor: Communicates with customers, schedules repairs, and provides estimates, requiring strong customer service and technical knowledge.
Advancing to these roles often requires completing a formal training program and obtaining certifications, such as those offered by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
4.3 Advanced Positions
- Master Technician: Holds advanced certifications and possesses expertise in diagnosing and repairing complex automotive issues.
- Shop Foreman: Supervises and coordinates the work of other technicians, ensuring quality and efficiency in the repair process.
These positions typically require several years of experience and ongoing training to stay current with new technologies and repair techniques.
4.4 Specialized Roles
- Diagnostic Technician: Uses advanced diagnostic equipment to identify and resolve difficult automotive problems.
- Electrical/Electronics Technician: Specializes in repairing and maintaining the electrical and electronic systems of vehicles.
- Transmission Technician: Focuses on the repair and rebuilding of transmissions.
- Body Repair Technician: Repairs collision damage and restores vehicles to their original condition.
Specialized roles often require additional training and certification in specific areas of automotive repair.
4.5 Business Ownership
- Auto Repair Shop Owner: Manages all aspects of an auto repair business, including customer service, technician supervision, and financial management.
Starting an auto repair shop requires a significant investment of time and money, as well as strong business management skills. According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), a well-prepared business plan is essential for securing funding and ensuring the success of the business.
5. Essential Skills for Success in Auto Repair
To excel in the auto repair industry, certain skills are essential. Here’s a breakdown of the key skills needed:
5.1 Technical Skills
- Diagnostic Skills: Ability to accurately diagnose automotive problems using diagnostic tools and techniques.
- Repair Skills: Proficiency in repairing various vehicle systems, including engines, transmissions, brakes, and electrical systems.
- Tool Proficiency: Competence in using a wide range of hand tools, power tools, and diagnostic equipment.
- Technical Knowledge: Understanding of automotive technology, including mechanical, electrical, and electronic systems.
5.2 Soft Skills
- Problem-Solving: Ability to analyze complex problems and develop effective solutions.
- Attention to Detail: Accuracy in performing repairs and inspections to ensure quality and safety.
- Communication: Clear and effective communication with customers and colleagues.
- Customer Service: Providing excellent customer service to build trust and loyalty.
- Time Management: Efficiently managing time to complete repairs in a timely manner.
5.3 Business Skills
- Financial Management: Understanding of financial statements, budgeting, and cost control.
- Marketing: Ability to attract and retain customers through effective marketing strategies.
- Management: Skills in managing employees, scheduling work, and ensuring quality control.
- Sales: Proficiency in selling repair services and products to customers.
6. Training and Certification Programs
Formal training and certification programs are crucial for advancing your career in auto repair. Here’s an overview of available options:
6.1 Vocational Schools
- Program Overview: Vocational schools offer hands-on training in automotive technology, covering basic and advanced repair techniques.
- Curriculum: The curriculum includes courses in engine repair, electrical systems, brakes, transmissions, and diagnostics.
- Benefits: Vocational schools provide practical training, industry-recognized certifications, and job placement assistance.
6.2 Community Colleges
- Program Overview: Community colleges offer associate degrees in automotive technology, providing a more comprehensive education in the field.
- Curriculum: The curriculum includes courses in automotive theory, diagnostics, and repair, as well as general education courses.
- Benefits: Community colleges offer affordable tuition, flexible scheduling, and transfer opportunities to four-year universities.
6.3 Apprenticeship Programs
- Program Overview: Apprenticeship programs combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction, allowing you to earn while you learn.
- Curriculum: The curriculum includes hands-on training in various aspects of automotive repair, as well as related coursework.
- Benefits: Apprenticeship programs provide valuable work experience, mentorship from experienced technicians, and a clear path to certification.
6.4 ASE Certification
- Overview: ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification is a widely recognized industry standard that demonstrates competency in specific areas of automotive repair.
- Benefits: ASE certification enhances your credibility, increases your earning potential, and improves your job prospects.
- Requirements: To become ASE certified, you must pass a written exam and have at least two years of relevant work experience.
6.5 Online Training Programs
- Program Overview: Online training programs offer flexible and convenient learning options for aspiring and experienced auto technicians.
- Curriculum: The curriculum includes courses in automotive technology, diagnostics, and repair, as well as interactive simulations and virtual labs.
- Benefits: Online training programs offer self-paced learning, affordable tuition, and access to industry experts.
7. Steps to Open Your Own Auto Repair Shop
Starting your own auto repair shop can be a rewarding but challenging endeavor. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
7.1 Develop a Business Plan
- Executive Summary: A brief overview of your business, including its mission, goals, and objectives.
- Company Description: Detailed information about your business, including its legal structure, ownership, and location.
- Market Analysis: Research on the auto repair industry, including market trends, competition, and target customers.
- Service Offerings: A description of the services you will offer, including routine maintenance, repairs, and diagnostics.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: A plan for attracting and retaining customers, including advertising, promotions, and customer service.
- Financial Projections: Forecasts of your revenue, expenses, and profits, including a break-even analysis and cash flow projections.
The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers resources and templates to help you develop a comprehensive business plan.
7.2 Secure Funding
- Personal Savings: Using your own savings to fund your business can reduce your reliance on external financing.
- Loans: Applying for a small business loan from a bank or credit union can provide the capital you need to start your business.
- Grants: Researching and applying for government grants and other funding opportunities can provide additional financial support.
- Investors: Seeking investments from angel investors or venture capitalists can provide a larger source of funding for your business.
7.3 Choose a Location
- Accessibility: Choose a location that is easily accessible to your target customers, with ample parking and convenient access to major roads.
- Visibility: Select a location that is highly visible, with clear signage and a prominent storefront.
- Demographics: Research the demographics of the surrounding area to ensure that it aligns with your target customer base.
- Competition: Consider the level of competition in the area and choose a location that is not oversaturated with auto repair shops.
- Zoning Regulations: Check local zoning regulations to ensure that your business is permitted in the chosen location.
7.4 Obtain Licenses and Permits
- Business License: Obtain a general business license from your city or county.
- Auto Repair License: Obtain a specific auto repair license from your state, which may require passing an exam and meeting certain qualifications.
- Environmental Permits: Obtain any necessary environmental permits for handling hazardous materials, such as used oil and refrigerants.
- Building Permits: Obtain any necessary building permits for renovations or construction on your shop.
7.5 Purchase Equipment and Supplies
- Diagnostic Equipment: Purchase diagnostic scanners, multimeters, and other equipment to diagnose automotive problems.
- Repair Tools: Purchase a wide range of hand tools, power tools, and specialty tools to perform repairs.
- Lifts and Jacks: Purchase hydraulic lifts and jacks to safely raise vehicles for repairs.
- Parts and Supplies: Establish relationships with parts suppliers to ensure access to quality parts and supplies.
- Office Equipment: Purchase computers, printers, and other office equipment to manage your business.
7.6 Hire and Train Staff
- Technicians: Hire qualified technicians with experience in diagnosing and repairing various vehicle systems.
- Service Advisors: Hire service advisors with strong customer service skills and technical knowledge.
- Administrative Staff: Hire administrative staff to manage your office, answer phones, and handle paperwork.
- Training: Provide ongoing training to your staff to ensure they stay current with new technologies and repair techniques.
7.7 Market Your Business
- Website: Create a professional website that showcases your services, location, and contact information.
- Online Advertising: Use online advertising platforms, such as Google Ads and social media, to reach potential customers.
- Local Partnerships: Partner with local businesses, such as car dealerships and insurance companies, to generate referrals.
- Community Events: Participate in community events to raise awareness of your business and build relationships with potential customers.
By following these steps, you can increase your chances of successfully opening and operating your own auto repair shop.
8. Understanding Auto Repair Business Finances
Managing the finances of an auto repair shop is crucial for long-term success. Here’s an overview of key financial aspects:
8.1 Startup Costs
- Real Estate: Costs associated with renting or purchasing a shop location.
- Equipment: Investment in diagnostic equipment, repair tools, and lifts.
- Inventory: Initial stock of parts and supplies.
- Licenses and Permits: Fees for obtaining necessary licenses and permits.
- Marketing: Costs for creating a website, advertising, and promoting your business.
8.2 Operating Expenses
- Rent or Mortgage: Monthly payments for your shop location.
- Utilities: Costs for electricity, water, and gas.
- Salaries: Wages for technicians, service advisors, and administrative staff.
- Inventory: Ongoing costs for purchasing parts and supplies.
- Insurance: Premiums for liability, property, and workers’ compensation insurance.
- Marketing: Ongoing costs for advertising and promoting your business.
8.3 Revenue Streams
- Labor: Charges for technicians’ time spent on repairs and maintenance.
- Parts: Revenue from selling parts to customers.
- Services: Revenue from performing services, such as oil changes, tire rotations, and diagnostics.
- Sales: Revenue from selling automotive products, such as tires, batteries, and accessories.
8.4 Pricing Strategies
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Calculating your costs for labor, parts, and overhead, and adding a markup to determine your prices.
- Competitive Pricing: Setting your prices based on what your competitors are charging.
- Value-Based Pricing: Setting your prices based on the perceived value of your services to your customers.
8.5 Financial Metrics
- Gross Profit Margin: The percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold.
- Net Profit Margin: The percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses, including operating expenses and taxes.
- Break-Even Point: The level of sales at which your revenue equals your expenses.
- Cash Flow: The movement of cash into and out of your business over a period of time.
Understanding these financial aspects can help you make informed decisions and manage your auto repair shop effectively.
9. Current Trends in the Auto Repair Industry
Staying updated with the latest trends in the auto repair industry is crucial for staying competitive. Here are some current trends:
9.1 Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Growth: The increasing popularity of EVs is driving demand for specialized EV repair and maintenance services.
- Training: Technicians need to be trained in EV technology, including battery maintenance, electric motor repair, and charging system diagnostics.
- Equipment: Shops need to invest in specialized equipment for servicing EVs, such as battery testers and high-voltage safety gear.
9.2 Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
- Features: ADAS features, such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking, are becoming increasingly common in new vehicles.
- Calibration: ADAS components require precise calibration after repairs or replacements to ensure they function correctly.
- Equipment: Shops need to invest in ADAS calibration equipment and training to properly service these systems.
9.3 Digitalization
- Software: Automotive repair is becoming increasingly reliant on software and digital tools, such as diagnostic scanners and online repair manuals.
- Connectivity: Vehicles are becoming more connected, with features such as over-the-air updates and remote diagnostics.
- Data Analysis: Shops can use data analytics to improve their efficiency, optimize their pricing, and personalize their marketing efforts.
9.4 Customer Experience
- Convenience: Customers are demanding more convenient and personalized service experiences, such as online scheduling, mobile payments, and vehicle pick-up and delivery.
- Transparency: Customers want to be informed about the repairs being performed on their vehicles and the associated costs.
- Communication: Shops need to communicate effectively with customers throughout the repair process, providing updates and answering their questions.
By staying informed about these trends, you can position your auto repair shop for success in the future.
10. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Running an auto repair shop comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common issues and solutions:
10.1 Competition
- Challenge: Facing competition from other auto repair shops in your area.
- Solution: Differentiate your business by offering specialized services, providing excellent customer service, and implementing effective marketing strategies.
10.2 Staffing
- Challenge: Recruiting and retaining qualified technicians and service advisors.
- Solution: Offer competitive wages, benefits, and training opportunities to attract and retain talented employees.
10.3 Rising Costs
- Challenge: Dealing with rising costs for parts, supplies, and insurance.
- Solution: Negotiate with suppliers to get better prices, implement cost-saving measures, and adjust your pricing to reflect rising costs.
10.4 Customer Satisfaction
- Challenge: Ensuring that customers are satisfied with the repairs and services they receive.
- Solution: Communicate clearly with customers, provide accurate estimates, and perform high-quality repairs in a timely manner.
10.5 Regulatory Compliance
- Challenge: Complying with environmental regulations, safety standards, and licensing requirements.
- Solution: Stay informed about regulatory changes, implement compliance procedures, and seek guidance from industry experts.
By anticipating these challenges and implementing proactive solutions, you can increase your chances of success in the auto repair industry.
At AUTO-REPAIR-TRAINING.EDU.VN, we’re dedicated to supporting your journey in the auto repair industry, whether you’re learning the basics or aiming to open your own shop. Our resources, training programs, and expert guidance are designed to help you succeed every step of the way.
FAQ: Auto Screen Repair & Auto Repair Career
Q1: What are the common causes of the Windows auto screen repair loop?
The Windows auto screen repair loop typically results from corrupted system files, faulty Boot Manager data, incompatible hardware configurations, or problematic Windows updates. Regular system maintenance can help prevent these issues.
Q2: How can I fix the auto screen repair loop on my Windows computer?
You can fix the auto screen repair loop by using System Restore, running built-in system repair tools (SFC and CHKDSK), performing antivirus scans, updating drivers in Safe Mode, disabling the automatic repair feature, or repairing the Boot Configuration Data (BCD).
Q3: What are the key skills needed to succeed in the auto repair industry?
Essential skills include technical expertise in diagnostics and repair, soft skills like problem-solving and customer service, and business acumen for financial management and marketing.
Q4: What training and certification programs are available for aspiring auto technicians?
Options include vocational schools, community colleges with automotive technology programs, apprenticeship programs, ASE certification, and online training programs.
Q5: What steps should I take to open my own auto repair shop?
Key steps include developing a comprehensive business plan, securing funding, choosing a suitable location, obtaining necessary licenses and permits, purchasing equipment and supplies, hiring and training staff, and marketing your business effectively.
Q6: How can I manage the finances of my auto repair shop effectively?
Manage your finances by understanding startup costs, operating expenses, and revenue streams. Implement effective pricing strategies and monitor key financial metrics like gross profit margin, net profit margin, and cash flow.
Q7: What are the current trends in the auto repair industry?
Current trends include the increasing popularity of electric vehicles (EVs), advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), digitalization of repair processes, and the need for enhanced customer experience.
Q8: What are some common challenges in running an auto repair shop, and how can I overcome them?
Common challenges include competition, staffing issues, rising costs, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. Overcome these by differentiating your business, offering competitive wages and benefits, negotiating with suppliers, communicating clearly with customers, and staying informed about regulatory changes.
Q9: How important is ASE certification for auto technicians?
ASE certification is highly important as it demonstrates competency and enhances credibility, leading to increased earning potential and better job prospects.
Q10: What is the potential income for an auto repair shop owner?
The potential income for an auto repair shop owner varies greatly depending on factors such as location, size, reputation, and management skills. According to industry reports, successful shop owners can earn six-figure incomes, but it requires significant effort and investment.
Ready to take the next step? Contact AUTO-REPAIR-TRAINING.EDU.VN today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 200 N Michigan Ave, Suite 1500, Chicago, IL 60601, United States. Let us help you achieve your goals in the auto repair industry with our comprehensive training and expert guidance. Visit AUTO-REPAIR-TRAINING.EDU.VN for more information.